Posted on: 22 Apr, 2024, 5:04 AM
Comprehensive Guide to Advertising Laws and Regulations in Japan
In Japan, advertising laws and regulations are designed to ensure fairness, transparency, and consumer protection. Here are the key points to understand when advertising in Japan:
General Regulatory Framework: Advertising in Japan is governed by several laws, including the Act against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations, the Health Promotion Law, and specific laws governing advertising in sectors like pharmaceuticals and financial services.
Consumer Protection: The Japan Fair Trade Commission (JFTC) enforces regulations against misleading advertisements and deceptive practices that can affect consumer decisions. Advertisements must not contain false or exaggerated claims and should provide clear and accurate information.
Substantiation of Claims: Advertisers are required to substantiate any claims they make in their advertisements, especially those related to product efficacy and safety. This includes having adequate evidence or studies to back up claims.
Comparative Advertising: Comparative advertising is permitted but must be fair and cannot mislead. Comparisons must be based on verifiable facts and should not unfairly disparage a competitor's products.
Special Rules for Pharmaceuticals and Alcohol: Strict rules regulate the advertising of pharmaceuticals, particularly prescription drugs, which can only be marketed to healthcare professionals. Alcohol advertising must not encourage excessive drinking and must not target minors.
Privacy and Data Protection: Advertisers using personal data must comply with Japan’s Act on the Protection of Personal Information, which requires proper handling and protection of personal data to avoid breaches of privacy.
Online and Digital Advertising: Online advertisements must follow the same rules as traditional media but also face additional scrutiny regarding privacy issues and data security, especially under recent amendments to the personal data protection law.
Self-Regulation: Besides governmental regulations, Japan has a strong tradition of industry self-regulation. Organizations like the Japan Advertising Review Organization (JARO) play a significant role in monitoring advertisements and handling consumer complaints.
Cultural Considerations: Advertisements in Japan should respect cultural norms and practices. This includes avoiding content that may be considered disrespectful or offensive, which can vary significantly from Western standards.
Trending

Elevate Your Brand in 2024 with Times Square's Top 3D Screens!
Unlock unparalleled brand visibility in New York City! Times Square, renowned for its vibrant digital landscape, presents an unique opportunity with its top four 3D screens: ‘Digital Godzilla’, ‘Big Kahuna’, ‘The Monsta’, and ‘Big Bertha’. Each screen offers a unique canvas for your brand to captivate millions with unmatched clarity, scale, and engagement. Whether it's the sheer size of ‘Big Kahuna’ or the innovative technology of ‘Digital Godzilla’, your advertisement will not just be seen; it will be an experience. Collaborate with GlobalMediaKit for tailored advertising solutions that breathe life into your brand at Times Square. Let's make your presence in one of the world's most iconic locations impactful.
Explore Now On: www.globalmediakit.com

Dive into Experiential Marketing with GlobalMediaKit!
Now in the UAE! Immerse your audience with experiential marketing. Transform your brand's narrative into an interactive journey, capturing attention with immersive art installations, live demonstrations, and exclusive events in the UAE. This innovative approach turns advertising into memorable encounters, heightening audience engagement and nurturing brand loyalty in the UAE. Embark on an advertising revolution in the UAE, where your brand is not just seen but deeply experienced. Collaborate with GlobalMediaKit to make your brand an unforgettable part of your target audience's daily life in the UAE. Connect with us now and achieve unmatched experiential marketing success in the UAE!
Explore now:www.globalmediakit.com
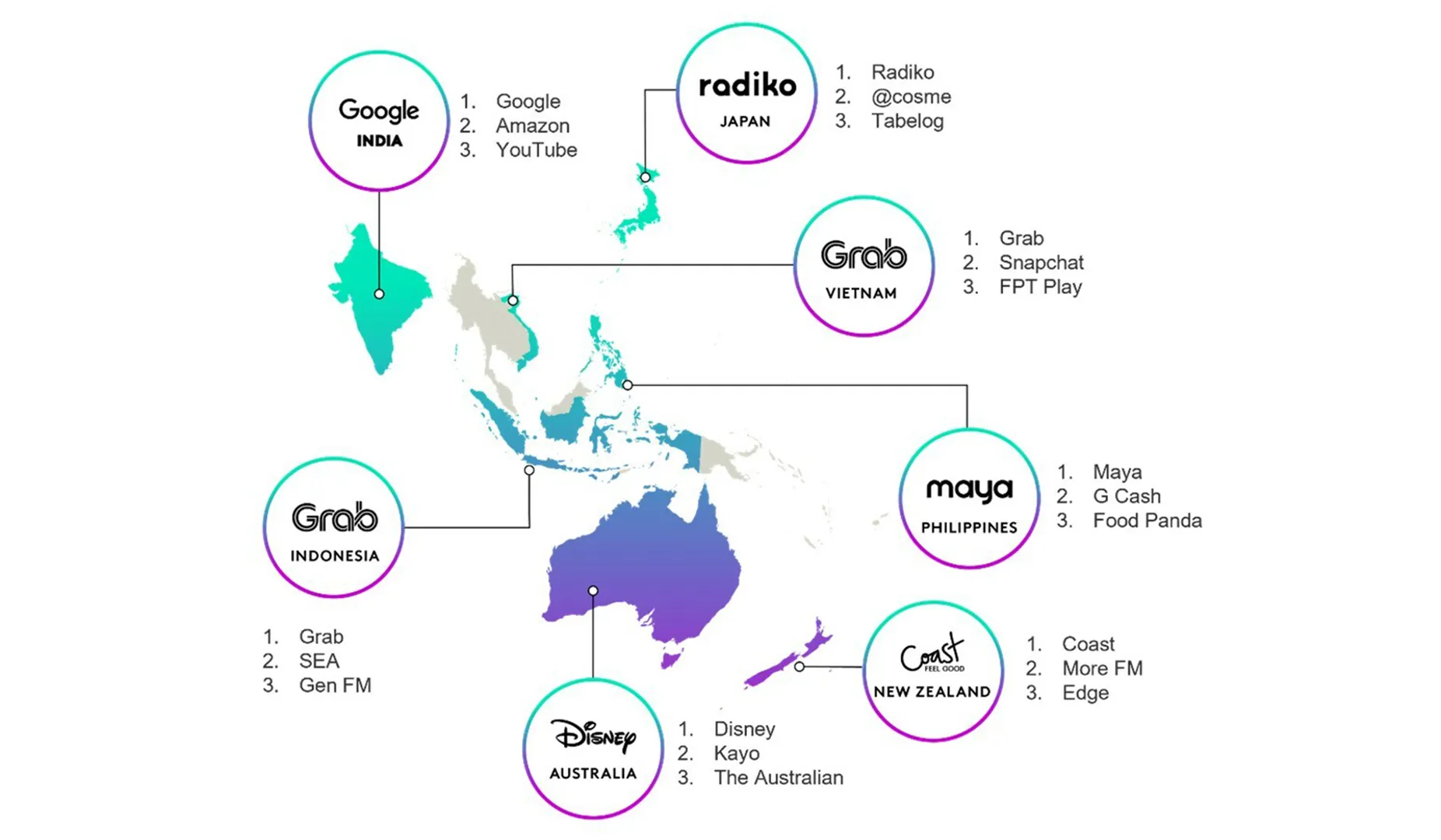




YouTube and Google Most Preferred Ad Platforms of Marketers in Asia Pacific
1/6/2024
Google continues to hold its top spot of being consumers' most preferred ad platform in Asia Pacific, according to Kantar. Most consumers view Google ads as relevant and helpful, as per Kantar Media Reactions 2023. Meanwhile, Google is APAC marketers' second-favourite platform while YouTube is the first in their list of preferences.
Source: PR Newswire
www.globalmediakit.com





Asia Pacific Leads the Way with the Presence of World's Top Four OOH Markets
1/6/2024
Speaking at WOO's second Asia Forum in Bali, World Out of Home Organization President Tom Goddard stated that Asia Pacific has the largest young population in the world, a GDP greater than that of either the US or Europe, and the most thriving Out-of-home business. Four of the largest OOH markets in the world can be found in APAC.
Source: World Out of Home Organization
www.globalmediakit.com





Saudi Arabia's 1,600 Taxis to Carry Ads, Opens New Revenue Streams
1/6/2024
Exciting news for advertisers: A deal permitting 1,600 taxis to carry advertisements has been signed by Saudi Arabia’s Transport General Authority. In addition to offering advertisers more choices, the contract aims to give taxi companies a new source of income. This is the Kingdom's first agreement of its kind.
Source: Arab News
www.globalmediakit.com





Asia's Video Market Expected to Hit 165 billion Dollars by 2028
1/6/2024
China Continues to Lead the Asia Pacific region with 64-billion-dollar revenue
A study by research and consulting firm Media Partners Asia projects that over the next five years, Asia's video market will expand at an annual rate of 2.6%, reaching $165 billion by 2028. With a revenue of $64 billion in 2023, China continues to be the largest and most regulated video market in the Asia Pacific region.
Source: Variety
www.globalmediakit.com





India's Small and Medium Businesses to Double its Digital Ad Spend by 100%
1/6/2024
In 2024, small and medium businesses (SMBs) in India are poised to leverage streaming TV extensively to achieve their marketing objectives. Amazon Ads, the advertising service of e-commerce giant Amazon, has confirmed this trend in the global advertising industry. Simultaneously, a FICCI-EY report has forecast a remarkable journey for SMBs in India, projecting their digital ad spend to double in just five years by 100 percent, beginning from the year 2022.
Source: Campaign India
www.globalmediakit.com
GLOBAL MEDIA KIT
The unique platform to plan, build and execute top-notch brand campaigns by discovering and securing leading ad opportunities through seamless partnership between advertisers and the dynamic global media.
RESOURCES
USEFUL LINKS