Posted on: 22 Apr, 2024, 5:04 AM
Overview of Advertising Regulations and Standards in India
In India, the advertising landscape is regulated through a combination of legislation and self-regulatory guidelines to protect consumers and ensure fair business practices. Here are some essential aspects of advertising laws in India:
Legislative Framework: The primary legislation includes the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, which has provisions specifically aimed at preventing unfair trade practices and misleading advertisements. It also establishes the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) which can penalize misleading ads.
Self-Regulation by ASCI: The Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI) plays a crucial role in self-regulating advertising standards. ASCI guidelines ensure that advertisements are not misleading, harmful, or offensive. They must be truthful, fair, and substantiate claims they make.
Substantiation of Claims: Advertisers are required to substantiate any claims they make in their ads to avoid misleading consumers. This includes claims about product features, health benefits, and pricing comparisons.
Prohibitions and Restrictions: Certain products and services have specific advertising restrictions. For example, tobacco advertising is banned, and there are strict regulations for advertising alcohol, pharmaceuticals, and infant food.
Digital Advertising: Digital advertising is subject to the Information Technology Act, 2000, which deals with cybercrimes and electronic commerce. The ASCI also has specific guidelines for digital media to ensure that online ads are fair and transparent.
Endorsements and Celebrity Advertising: The ASCI guidelines stipulate that celebrities or influencers who endorse products must have adequate knowledge or experience with the product, ensuring that endorsements are not misleading.
Telemarketing and Spam: The Telecom Commercial Communications Customer Preference Regulations, 2018, govern telemarketing activities, requiring telemarketers to register and adhere to guidelines that prevent spam and protect consumer privacy.
Cultural Sensitivity: Advertisements in India must respect the diverse cultural, religious, and socio-economic sentiments of the public. Content that could be construed as offensive or disrespectful to any community is not only frowned upon but can also lead to legal trouble.
Trending

Elevate Your Brand in 2024 with Times Square's Top 3D Screens!
Unlock unparalleled brand visibility in New York City! Times Square, renowned for its vibrant digital landscape, presents an unique opportunity with its top four 3D screens: ‘Digital Godzilla’, ‘Big Kahuna’, ‘The Monsta’, and ‘Big Bertha’. Each screen offers a unique canvas for your brand to captivate millions with unmatched clarity, scale, and engagement. Whether it's the sheer size of ‘Big Kahuna’ or the innovative technology of ‘Digital Godzilla’, your advertisement will not just be seen; it will be an experience. Collaborate with GlobalMediaKit for tailored advertising solutions that breathe life into your brand at Times Square. Let's make your presence in one of the world's most iconic locations impactful.
Explore Now On: www.globalmediakit.com

Dive into Experiential Marketing with GlobalMediaKit!
Now in the UAE! Immerse your audience with experiential marketing. Transform your brand's narrative into an interactive journey, capturing attention with immersive art installations, live demonstrations, and exclusive events in the UAE. This innovative approach turns advertising into memorable encounters, heightening audience engagement and nurturing brand loyalty in the UAE. Embark on an advertising revolution in the UAE, where your brand is not just seen but deeply experienced. Collaborate with GlobalMediaKit to make your brand an unforgettable part of your target audience's daily life in the UAE. Connect with us now and achieve unmatched experiential marketing success in the UAE!
Explore now:www.globalmediakit.com
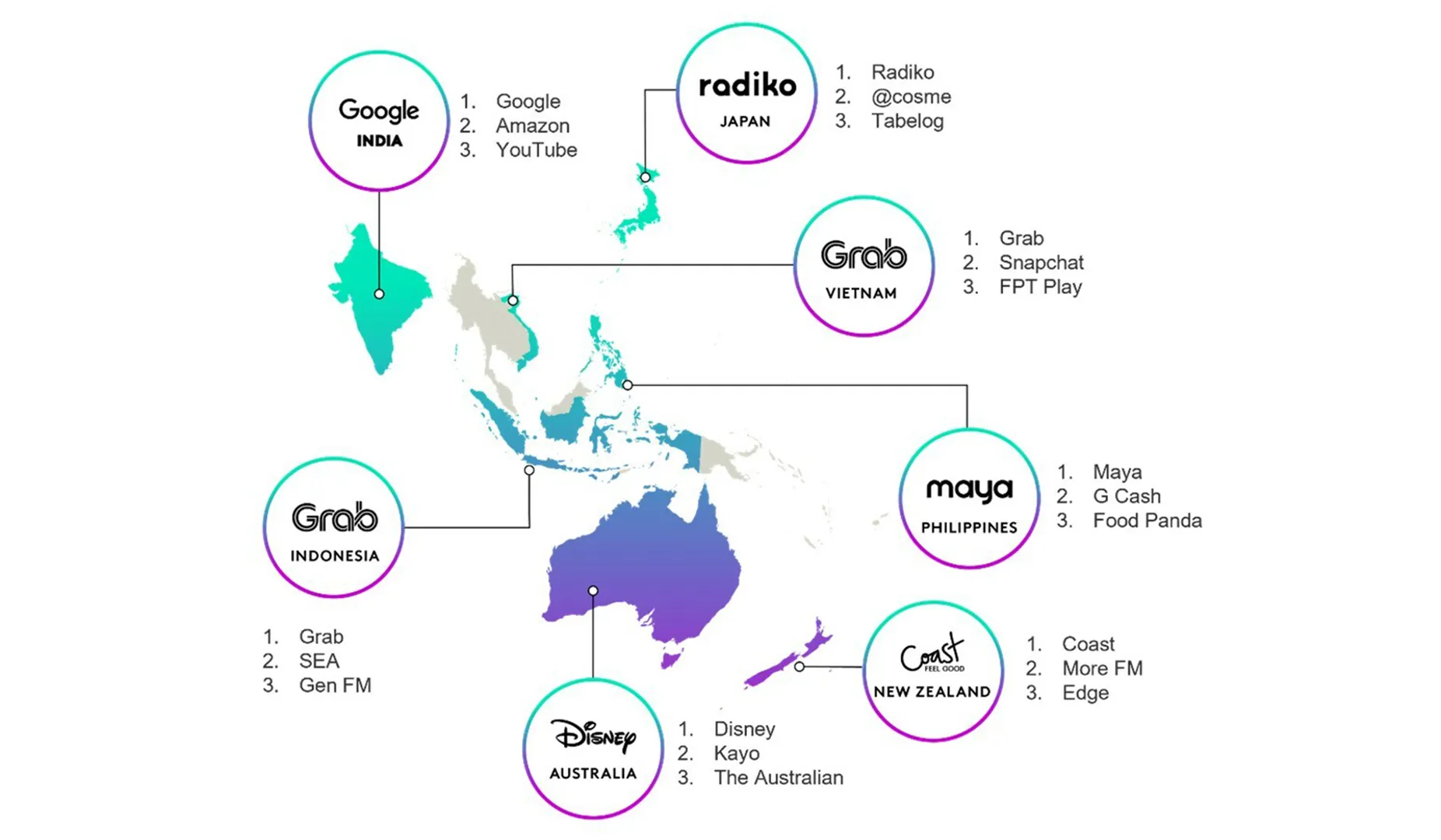




YouTube and Google Most Preferred Ad Platforms of Marketers in Asia Pacific
1/6/2024
Google continues to hold its top spot of being consumers' most preferred ad platform in Asia Pacific, according to Kantar. Most consumers view Google ads as relevant and helpful, as per Kantar Media Reactions 2023. Meanwhile, Google is APAC marketers' second-favourite platform while YouTube is the first in their list of preferences.
Source: PR Newswire
www.globalmediakit.com





Asia Pacific Leads the Way with the Presence of World's Top Four OOH Markets
1/6/2024
Speaking at WOO's second Asia Forum in Bali, World Out of Home Organization President Tom Goddard stated that Asia Pacific has the largest young population in the world, a GDP greater than that of either the US or Europe, and the most thriving Out-of-home business. Four of the largest OOH markets in the world can be found in APAC.
Source: World Out of Home Organization
www.globalmediakit.com





Saudi Arabia's 1,600 Taxis to Carry Ads, Opens New Revenue Streams
1/6/2024
Exciting news for advertisers: A deal permitting 1,600 taxis to carry advertisements has been signed by Saudi Arabia’s Transport General Authority. In addition to offering advertisers more choices, the contract aims to give taxi companies a new source of income. This is the Kingdom's first agreement of its kind.
Source: Arab News
www.globalmediakit.com





Asia's Video Market Expected to Hit 165 billion Dollars by 2028
1/6/2024
China Continues to Lead the Asia Pacific region with 64-billion-dollar revenue
A study by research and consulting firm Media Partners Asia projects that over the next five years, Asia's video market will expand at an annual rate of 2.6%, reaching $165 billion by 2028. With a revenue of $64 billion in 2023, China continues to be the largest and most regulated video market in the Asia Pacific region.
Source: Variety
www.globalmediakit.com





India's Small and Medium Businesses to Double its Digital Ad Spend by 100%
1/6/2024
In 2024, small and medium businesses (SMBs) in India are poised to leverage streaming TV extensively to achieve their marketing objectives. Amazon Ads, the advertising service of e-commerce giant Amazon, has confirmed this trend in the global advertising industry. Simultaneously, a FICCI-EY report has forecast a remarkable journey for SMBs in India, projecting their digital ad spend to double in just five years by 100 percent, beginning from the year 2022.
Source: Campaign India
www.globalmediakit.com
GLOBAL MEDIA KIT
The unique platform to plan, build and execute top-notch brand campaigns by discovering and securing leading ad opportunities through seamless partnership between advertisers and the dynamic global media.
RESOURCES
USEFUL LINKS